Misc
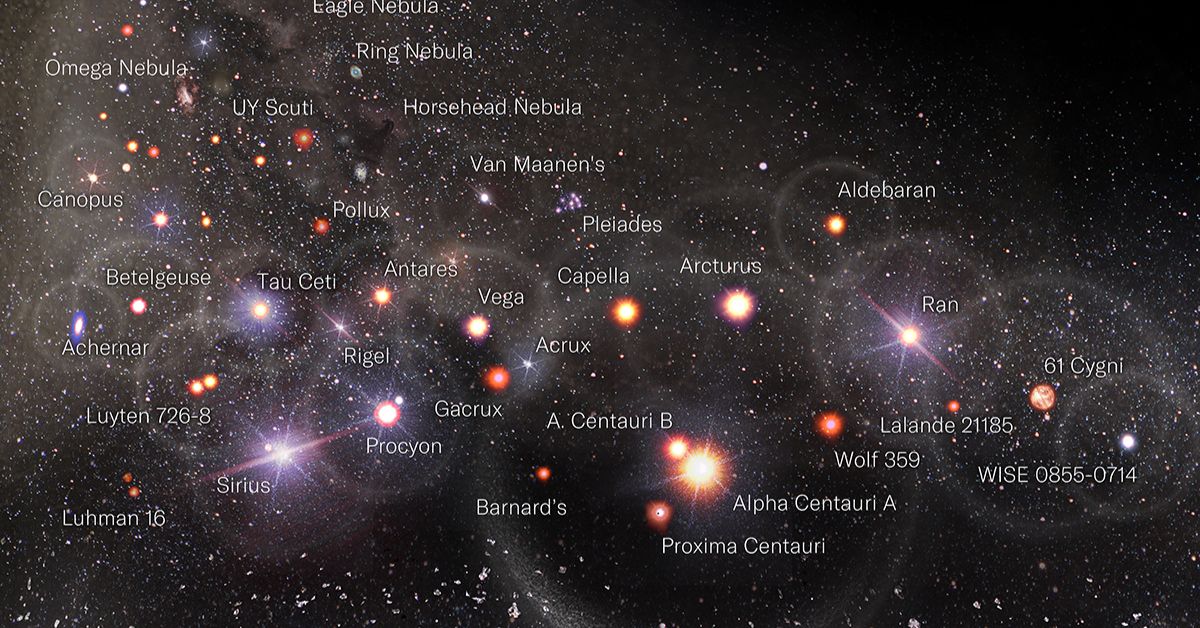
A Logarithmic Map of the Entire Observable Universe

For a full-size option or to inquire about posters, please visit Pablo Carlos Budassi’s website.
A Logarithmic Map of the Entire Observable Universe
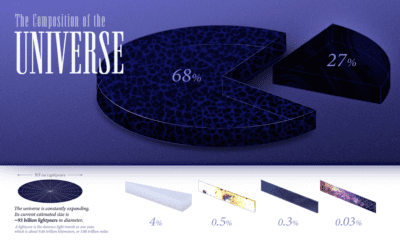
Among the scientific community, it’s widely believed that so far humans have only discovered about 5% of the universe.
Yet, despite knowing about just a fraction of what’s out there, we’ve still managed to discover galaxies billions of light-years away from Earth.
This graphic by Pablo Carlos Budassi provides a logarithmic map of the entire known universe, using data by researchers at Princeton University and updated as of May 2022.
How Does the Map Work?
Before diving in, it’s worth touching on a few key details about the map.
First off, it’s important to note that the celestial objects shown on this map are not shown to scale. If it was made to scale with sizes relative to how we see them from Earth, nearly all of the objects would be miniscule dots (except the Moon, the Sun, and some nebulae and galaxies).
Secondly, each object’s distance from the Earth is measured on a logarithmic scale, which increases exponentially, in order to fit in all the data.
Within our Solar System, the map’s scale spans astronomical units (AU), roughly the distance from the Earth to the Sun. Beyond, it grows to measure millions of parsecs, with each one of those equal to 3.26 light-years, or 206,000 AU.
Exploring the Map
The map highlights a number of different celestial objects, including:
- The Solar System
- Comets and asteroids
- Star systems and clusters
- Nebulae
- Galaxies, including the Milky Way
- Galaxy clusters
- Cosmic microwave background—radiation leftover from the Big Bang
Featured are some recently discovered objects, such as the most distant known galaxy to date, HD1. Scientists believe this newly-discovered galaxy was formed just 330 million years after the Big Bang, or roughly 8.4 billion years before Earth.
It also highlights some newly deployed spacecraft, including the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), which is NASA’s latest infrared telescope, and the Tiangong Space Station, which was made by China and launched in April 2021.
Why is it called the “Observable” Universe?
Humanity has been interested in space for thousands of years, and many scientists and researchers have dedicated their lives to furthering our collective knowledge about space and the universe.
Most people are familiar with Albert Einstein and his theory of relativity, which became a cornerstone of both physics and astronomy. Another well-known scientist was Edwin Hubble, whose findings of galaxies moving away from Earth is considered to be the first observation of the universe expanding.
But the massive logarithmic map above, and any observations from Earth or probes in space, are limited in nature. The universe is currently dated to be around 13.8 billion years old, and nothing in the universe can travel faster than the speed of light.
When accounting for the expansion of the universe and observed objects moving away from us, that means that the farthest we can “see” is currently calculated at around 47.7 billion light-years. And since light takes time to travel, much of what we’re observing actually happened many millions of years ago.
But our understanding of the universe is evolving constantly with new discoveries. What will we discover next?

This article was published as a part of Visual Capitalist's Creator Program, which features data-driven visuals from some of our favorite Creators around the world.
United States
Charted: What Southeast Asia Thinks About China & the U.S.
A significant share of respondents from an ASEAN-focused survey are not happy about rising American and Chinese influence in the region.
What Southeast Asia Thinks About China & the U.S.
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
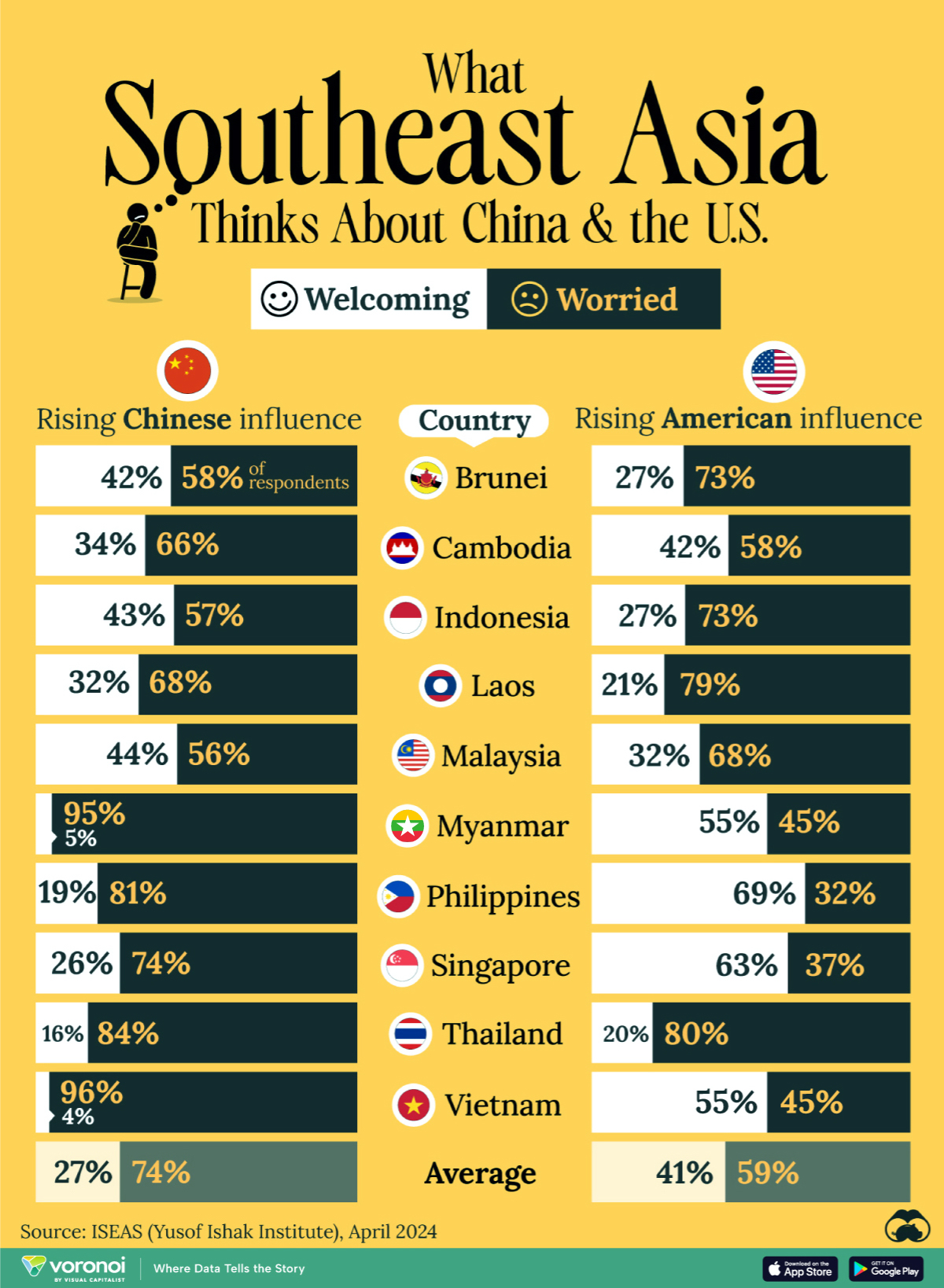
This chart visualizes the results of a 2024 survey conducted by the ASEAN Studies Centre at the ISEAS-Yusof Ishak Institute. Nearly 2,000 respondents were asked if they were worried or welcoming of rising Chinese and American geopolitical influence in their country.
The countries surveyed all belong to the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN), a political and economic union of 10 states in Southeast Asia.
Feelings Towards China
On average, a significant share of respondents from all 10 countries are worried about rising influence from both the U.S. and China.
However, overall skepticism is higher for China, at 74% (versus 59% for U.S.).
| Country | Worried About Growing 🇨🇳 Influence | Welcome Growing 🇨🇳 Influence |
|---|---|---|
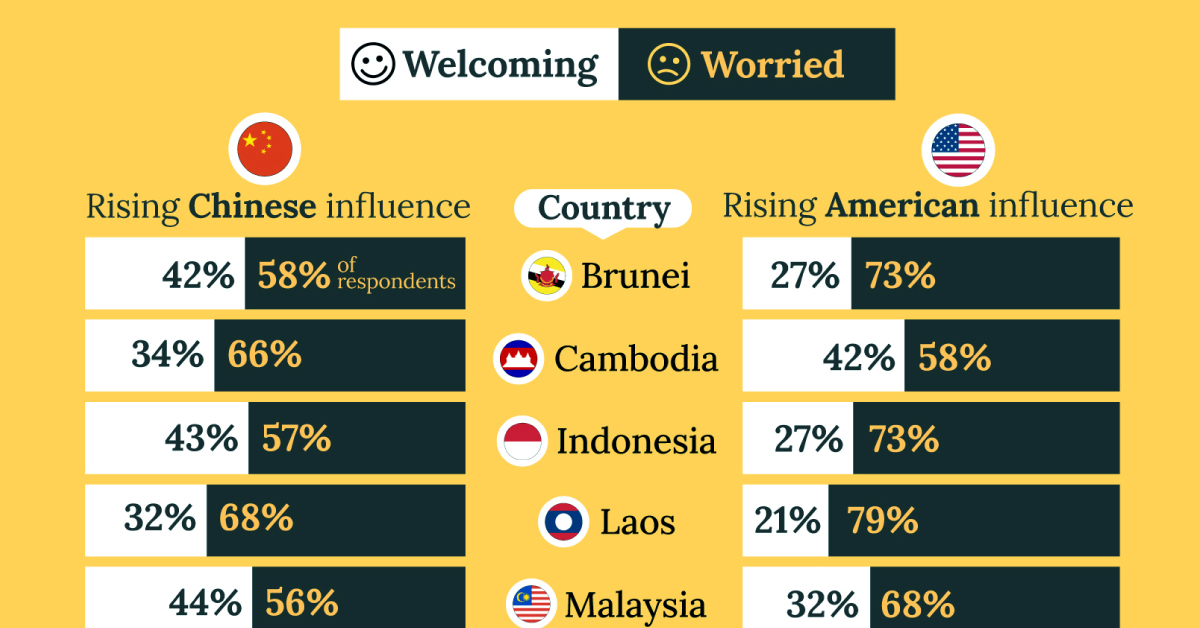
| 🇧🇳 Brunei | 58% | 42% |
| 🇰🇭 Cambodia | 66% | 34% |
| 🇮🇩 Indonesia | 57% | 43% |
| 🇱🇦 Laos | 68% | 32% |
| 🇲🇾 Malaysia | 56% | 44% |
| 🇲🇲 Myanmar | 95% | 5% |
| 🇵🇭 Philippines | 81% | 19% |
| 🇸🇬 Singapore | 74% | 26% |
| 🇹🇭 Thailand | 84% | 16% |
| 🇻🇳 Vietnam | 96% | 4% |
| Average | 74% | 27% |
The recently-cooled but still active territorial concerns over the South China Sea may play a significant role in these responses, especially in countries which are also claimants over the sea.
For example, in Vietnam over 95% of respondents said they were worried about China’s growing influence.
Feelings Towards America
Conversely, rising American influence is welcomed in two countries with competing claims in the South China Sea, the Philippines (69%) and Vietnam (55%).
| Country | Worried About Growing 🇺🇸 Influence | Welcome Growing 🇺🇸 Influence |
|---|---|---|
| 🇧🇳 Brunei | 73% | 27% |
| 🇰🇭 Cambodia | 58% | 42% |
| 🇮🇩 Indonesia | 73% | 27% |
| 🇱🇦 Laos | 79% | 21% |
| 🇲🇾 Malaysia | 68% | 32% |
| 🇲🇲 Myanmar | 45% | 55% |
| 🇵🇭 Philippines | 32% | 69% |
| 🇸🇬 Singapore | 37% | 63% |
| 🇹🇭 Thailand | 80% | 20% |
| 🇻🇳 Vietnam | 45% | 55% |
| Average | 59% | 41% |
Despite this, on a regional average, more respondents worry about growing American influence (59%) than they welcome it (41%).
Interestingly, it seems almost every ASEAN nation has a clear preference for one superpower over the other.
The only exception is Thailand, where those surveyed were not a fan of either option, with 84% worried about China, and 80% worried about the U.S.
-

 Culture6 days ago
Culture6 days agoThe World’s Top Media Franchises by All-Time Revenue
-

 Science2 weeks ago
Science2 weeks agoVisualizing the Average Lifespans of Mammals
-

 Brands2 weeks ago
Brands2 weeks agoHow Tech Logos Have Evolved Over Time
-

 Energy2 weeks ago
Energy2 weeks agoRanked: The Top 10 EV Battery Manufacturers in 2023
-

 Countries2 weeks ago
Countries2 weeks agoCountries With the Largest Happiness Gains Since 2010
-

 Economy2 weeks ago
Economy2 weeks agoVC+: Get Our Key Takeaways From the IMF’s World Economic Outlook
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoThe Countries That Have Become Sadder Since 2010
-

 Money1 week ago
Money1 week agoCharted: Who Has Savings in This Economy?